How Does Water Affect The Earth?
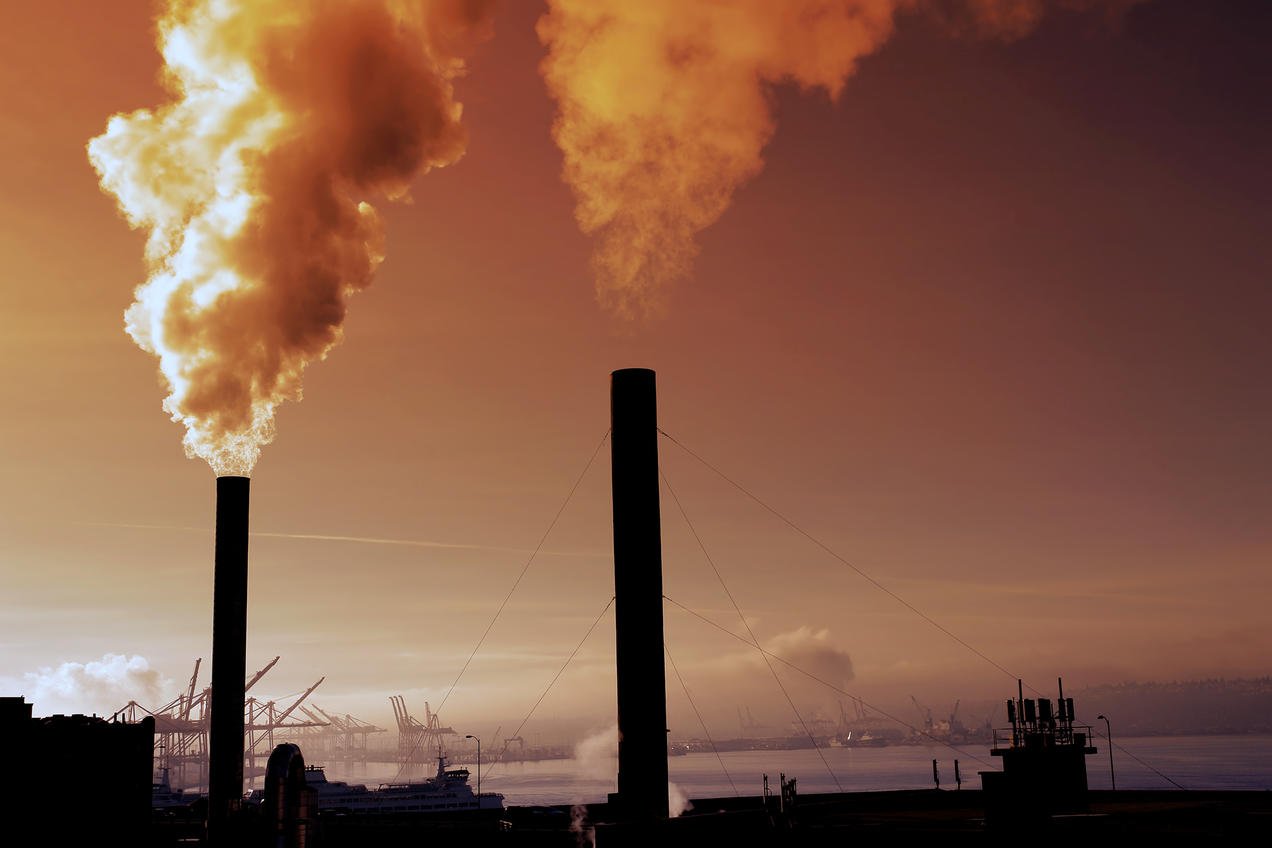
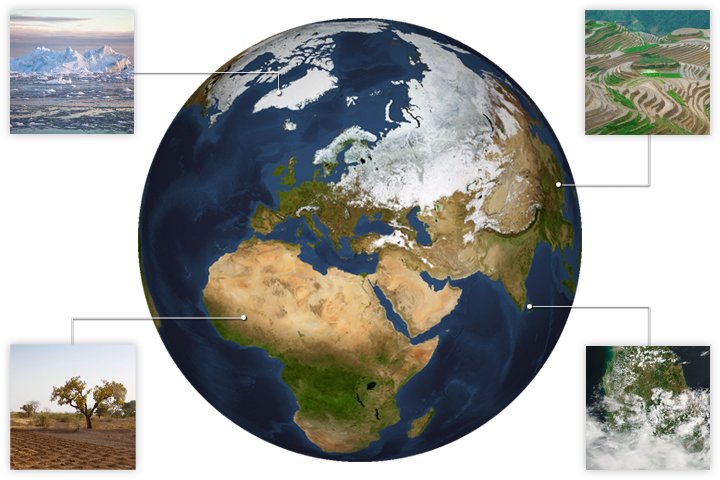
Water is a crucial element for life on Earth. It covers about 70% of the Earth’s surface and plays a vital role in many of the planet’s natural processes. In this article, we will explore how water affects the Earth and the ways in which it shapes our planet.
What Are The Ways Water Affects The Earth?
One of the most important ways that water affects the Earth is through the water cycle. This cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, is the process by which water is continually recycled through the atmosphere, oceans, and land. Water evaporates from the oceans and other bodies of water, rising into the atmosphere as water vapor. As the vapor cools, it condenses into clouds, which can then release the water as precipitation in the form of rain or snow. This water then flows back into the oceans or collects on land, where it can be used by plants and animals or seep into the ground to become part of the groundwater.
The Water Cycle
The water cycle plays a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate. Water vapor in the atmosphere acts as a greenhouse gas, trapping heat and keeping the planet warm. Without the water cycle, the Earth would be a much colder place, making it inhospitable for many forms of life. The water cycle also helps to regulate the temperature of the planet, ensuring that it doesn’t get too hot or too cold.
In addition to its role in the water cycle, water also plays a key role in shaping the Earth’s surface. Water is constantly eroding and reshaping the land, carving out rivers and streams and creating the many lakes and oceans that we see today. Water also helps to break down rocks and minerals, forming the soil that plants need to grow.
Conclusion
Water is also essential for life on Earth. All living things need water to survive, and many plants and animals are adapted to specific types of water environments. For example, some plants and animals live in freshwater environments, while others are adapted to saltwater environments. Water also plays a crucial role in many of the chemical reactions that take place within living organisms, helping to support the various metabolic processes that allow them to grow and thrive.